The following method has Share GPS listen for connections
and has the PC connect to it. For a potentially more
automated way by going in the other direction, skip to next
section.
-
Make sure the Linux PC is setup for Bluetooth. Check
for these packages:
-
BlueZ - core bluetooth package for most distributions
-
gpsd - helper program that can distribute GPS data
-
blueman - most useful GUI manager program
(gnome's manager isn't detailed enough)
-
Setup the Linux PC to be discoverable in it's Bluetooth
settings.
-
In Share GPS, create a new connection for NMEA Bluetooth
and set it up to Auto Find devices.
-
Pick the device from the list. If it has not been paired
Share GPS will attempt to start the pairing process.
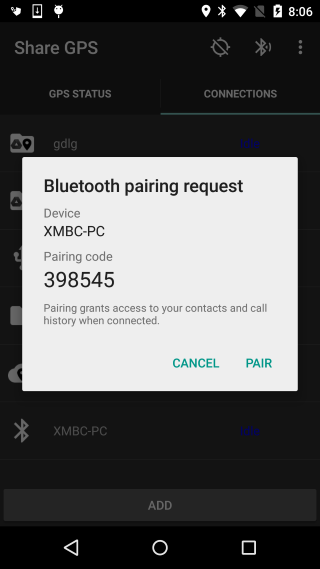
-
Start the connection in Share GPS. It will default to
a listening mode.
-
In Blueman, select the device and go to Device ->
ShareGPS and connect. If
the mobile is not in the list, make it discoverable by
using the icon in the ShareGPS navigation bar. Then use
Adapter->Search to find the mobile.
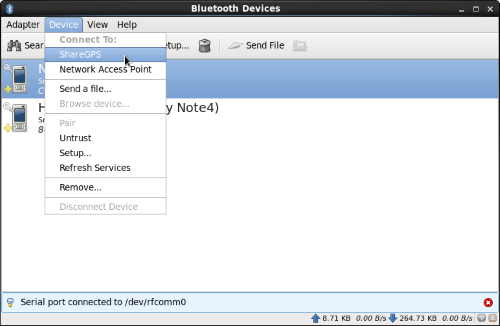
-
The serial port should indicate
connected to the serial port, something like /dev/rfcomm0.
-
If you do not have Blueman (or Blueman is giving you
issues) and need to use the command
line, do the following commands:
-
[root@tc01 ~]# hcitool scan
Scanning ...
C4:43:8F:A1:19:DA Nexus 5
5C:F3:70:6C:FA:61 XMBC-PC
-
sdptool browse C4:43:8F:A1:19:DA
In the output that follows, find the entry for
Share GPS and note the channel number, it is used
next
Service Name: ShareGPS
Service RecHandle: 0x1000d
Service Class ID List:
"Serial Port" (0x1101)
Protocol Descriptor List:
"L2CAP" (0x0100)
"RFCOMM" (0x0003)
Channel: 5
-
Start the connection in Share GPS. It will default to
a listening mode.
-
rfcomm connect /dev/rfcomm1 C4:43:8F:A1:19:DA 5
-
Share GPS should indicate Connected.
-
Start GPSD on the correct serial port
gpsd -N -n -b /dev/rfcomm1
-
Now start the GPSD compatible program, such as OpenCPN
-
The Linux version of Google Earth does not support NMEA
over a serial port. For that, we need to convert to
a KML.
-
To read NMEA directly without GPSD, try
this python script
with the serial port and desired kml file specified.
python ge.py /dev/rfcomm1 ./gps.kml
The python-serial module (pyserial) needs to be
installed, how this is done depends on the
distribution
-
To read data from GPSD, use
this python script
desired kml file specified.
python gpsd.py ./gps.kml
The following method has the PC listen for connections
and has Share GPS connect. This can be useful as the PC can
be setup to start listening on boot and automatically start
gpsd as needed. By doing this, the user
never has to touch the linux PC, so it is good for headless
systems. Using the tools here depends on the user having
systemd as their init system. Most of the popular
distributions have or are moving to this system.
-
Grab the following file from the Downloads page:
bt-gps.tar.gz
Unzip in a convenient location.
-
Run install.sh as root or sudo.
[user@tc01 ~]# sudo ./install.sh
-
The script will perform the following tasks:
-
Finds an open bluetooth channel to setup Serial
Port Profile on. Uses command
sdp browse local
If the command is not working, it will attempt
to have the bluetooth service run in compatibility
mode
-
Finds an open rfcomm device to use for bluetooth
connections
-
Install services for listening to bluetooth
connections and starting gpsd on socket access.
-
The following files are created:
-
/usr/local/bin/bt_gps.sh
-
/etc/systemd/system/bt-gps.service
-
/etc/systemd/system/bt-gpsd.service
-
/etc/systemd/system/bt-gpsd.socket
-
Then the systemd daemon control is restarted as well
as starting the bt-gps service.
-
If the script did not find sdptool, gpsd, or rfcomm, edit
the file /usr/local/bin/bt_gps.sh
with the full location to the binaries. If gpsd is not
found, edit the file
/etc/systemd/system/bt-gpsd.service with
the full path.
-
If any changes were needed, restart the service
systemctl restart bt-gps
-
Now the PC is listening for bluetooth connections
-
Start Share GPS and then re-pair the phone with the PC.
This is necessary so that Share GPS knows the channel
the PC is listening on.
-
Once the phone is re-paired, start the connection. It
will start in a Listening mode.
-
Now long press the connection and press Connect. The
status should then go to Connected.
-
Once the phone is connected, a listening socket is
started on port 2147 for GPSD. As soon as a client
tries to connect to the port, GPSD should start.
-
To test things, try using one of the gpsd example clients.
Run xgps & and verify you get
coordinates in xgps.
-
If wanting to use KML files, see previous section for a
python script that can help.
Troubleshooing
-
If having trouble with bluetooth connections, try things like
un-pairing the phone on both sides, turn bluetooth on and off,
airplane mode and back, etc, etc. Get back to square one and
re-pair, just be sure Share GPS is running on the mobile
and the bt-gps service is running on the PC.


